Extract from this study that describes step by step how to check for 5AR2 mutation at the genetic level, should you wish to pursue such testing (ie, use it to convince docs it is possible).
Steroid 5a -reductase type-2 Gene Mutations in the Turkish Population
turkjem.org/sayilar/17/13-19.pdf
HORMONES/METABOLITES
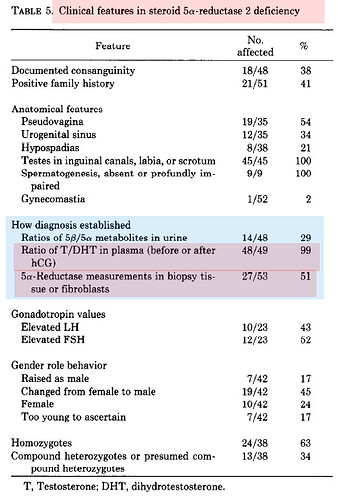
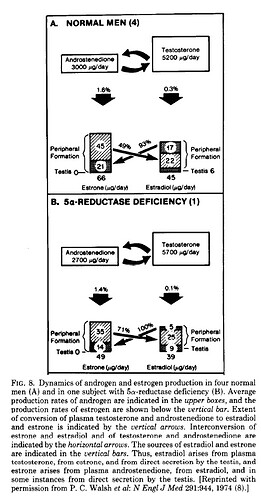
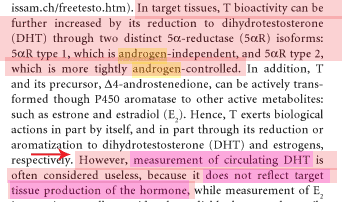
… “Plasma testosterone levels are elevated
and DHT levels are decreased in 5a-reductase
deficiency. Plasma T/DHT ratio is elevated”
… “Measurements of T and
DHT in serum after hCG stimulation, with determination
of T/DHT ratios are required to establish
the diagnosis. Assessment of urinary excretion of
5a/5b-steroid metabolites as well as measurement
of 5a-reductase enzyme activity in cultured genital
skin fibroblasts are ancillary investigations. All of
these parameters are highly variable in prepubertal
children and interpretation may be difficult. Therefore,
it is crucial to perform molecular genetic
analysis as an additional means for an accurate
diagnosis.”
GENETIC TESTING METHODS
- "…[b]screening of each exon for the etiologic mutation
was performed by SSCP analysis /b. This method
was first described by Orita and coworkers in 1989
and is based on the principle of identical electrophoretic
mobility of identical single stranded DNA
molecules (19).
The wild type and mutant DNA
are not identical; therefore they have different
mobility on a gel. SSCP technique has sensitivity
close to 100% if stringent conditions are used. This
feature permits accurate identification of normal,
homozygous and heterozygous individuals. The
drawback of this method is the requirement of
radioactive nucleotides (a-32P dATP) during the
experiment with its problems of availability and
high cost.
- Hiort and coworkers successfully used
denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) to
screen for mutations (10). This method requires no
radioactivity. Experience in molecular genetics is
needed to accurately perform DGGE.
When SSCP or DGGE finds an abnormal exon, the mutation
should be characterized by DNA sequencing.
-
An alternative approach is the sequencing of the whole
gene without employing screening. This is a more
costly way to detect mutations.
Above mentioned methods are used for searching unknown mutations.
-
If the causative mutation is already known, restriction
length fragment polymorphisms (RLFP), an easier
and faster method can be utilized to identify
patients, carriers and normals. -
The last step of the molecular genetic approach is the
determination of the functional significance of the mutation.
This is achieved by site-directed mutagenesis and invitro
transfection analysis.
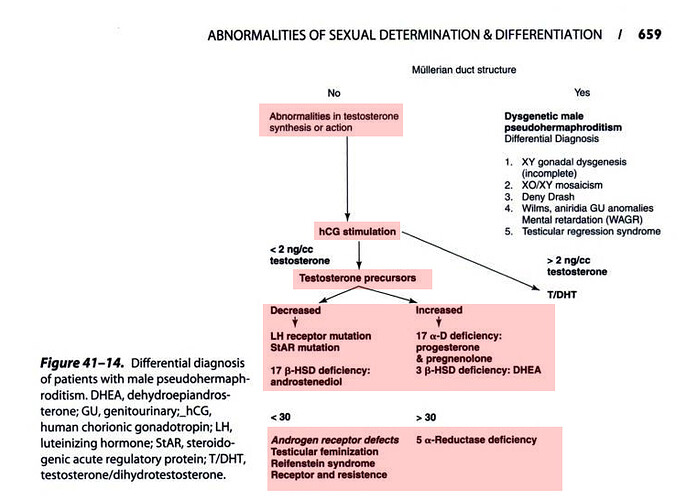
Mechanisms that adversely
alter the enzyme function must be delineated prior
to genetic counseling or prenatal diagnosis. Localization
or type of mutation may be responsible for severity
of enzyme dysfunction.
A structural change within
the enzyme results in a major dysfunction, as
evidenced by the severe phenotypic abnormalities
and elevated T/DHT ratio found in 5a-reductase
deficient male pseudohermaphrodites.