Link to article: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/121421728/abstract?CRETRY=1&SRETRY=0
Abstract below:
J Sex Med. 2008 Dec;5(12):2917-24.
[b]5-alpha reductase inhibitors and erectile dysfunction: the connection.[/b]
Erdemir F, Harbin A, Hellstrom WJ.
Tulane University-Department of Urology, New Orleans, LA, USA.
[b]INTRODUCTION:[/b] Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common problem affecting middle-aged and elderly men. First-line medical therapy includes alpha 1blockers and 5alpha-reductase inhibitors (5ARIs), such as finasteride and dutasteride. 5ARI use has been associated with adverse sexual outcomes, including erectile dysfunction (ED), ejaculatory dysfunction (EjD), and decreased libido.
AIM: To clarify the association between sexual adverse effects (AEs) and 5ARIs through review of literature concerning 5ARIs and to review the proposed mechanisms of these effects.
METHODS: A comprehensive literature review, using MEDLINE and PUBMED search engines, was conducted for all publications concerning 5ARIs and sexual AEs.
MAIN OUTCOME MEASURE: Sexual adverse effects, such as ED, EjD, and decreased libido, were the measured outcomes of this literature review.
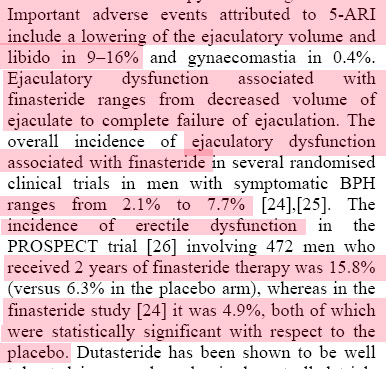
RESULTS: [Size=4]Sexual AEs are reported in clinical trials at rates of 2.1% to 38%[/size]. The most common sexual AE is ED, followed by EjD and decreased libido. These effects occur early in therapy and attenuate over time. [Size=4]A proposed mechanism for sexual dysfunction involves decreased nitric oxide synthase activity due to decreased dihydrotestosterone[/size].
CONCLUSIONS: [b]The connection between 5ARIs and sexual dysfunction is apparent upon review of the literature. [Size=4]Though theories have been proposed, little is known about the exact mechanisms behind 5ARI-related sexual dysfunction. [/size]
[Size=4]Since the connection between 5ARIs and sexual AEs is established in the literature, future research should be directed toward deciphering the pathophysiologic mechanisms. [/size]
When more basic science knowledge is attained in this area, [Size=4]the focus can shift toward prevention and treatment[/size][/b].
PMID: 19090946